Chemistry
Here, we will cover the various topics regarding the Subject Chemistry for Class 10. The concepts that are mastered in the lower classes help us to crack many entrance exams like JEE Main, JEE Advanced, etc. At ABHYASONLINE. IN you can master the concepts at your own learning pace. It provides conceptual testing with an analytical report identifying the weak, moderate and strong concepts. The student can revise the weak concepts with the help of videos and can attempt the remedial test to know the present level of understanding. We at ABHYASONLINE believe that if the weak concepts are identified and improved then every student can achieve their goals in life. Follow the links below to master each and every concept of various topics in Chemistry along with video lectures.
Explore Chapters
Chemical Reaction are represented in symbolic form by a Chemical equation. The reactants and the products are written in the form of symbols and formulae, wherein the reactant entities are given on the left-hand side and the product entities on the right-hand side. In this section of Chemical Reactions Advantages of using a chemical reaction, Balanced and Unbalanced Chemical Equation, Change in Colour, Temperature, Characteristics of chemical Reactions, Chemical changes, Chemical Equation, Corrosion, Endothermic and Exothermic Reaction, Evolution of gas, Formation of precipitate, How to make equations more informative, Information conveyed by a chemical equation, Limitations of chemical Reaction, Physical Change, Physical State, Product, Reactant, Types of changes, , etc. have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
- Sample Test(s)Test NameSubject(s)Topics / ChaptersQuestions / MarksActionMOCK (F) - 10th - Chemistry [Chemical Reactions I, Chemical Reactions II]ChemistryChemical Reactions I, Chemical Reactions II10 / 10Tutorial - 10th - Chemistry [Chemical Reactions I]ChemistryChemical Reactions I10 / 10View All FREE Test(s)
Chemical Reaction are represented in symbolic form by a Chemical equation. The reactants and the products are written in the form of symbols and formulae, wherein the reactant entities are given on the left-hand side and the product entities on the right-hand side. In this section of Chemical Reactions Combination Reaction, Decomposition Reaction, Displacement Reaction, Quicklime and Slaked Lime, Rancidity, Redox Reaction, Representation of Chemical Reaction, etc. have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
- Sample Test(s)Test NameSubject(s)Topics / ChaptersQuestions / MarksActionMOCK (F) - 10th - Chemistry [Chemical Reactions I, Chemical Reactions II]ChemistryChemical Reactions I, Chemical Reactions II10 / 10Tutorial - 10th - Chemistry [Chemical Reactions II]ChemistryChemical Reactions II10 / 10View All FREE Test(s)
An acid and a base are substances in chemistry. The aqueous solution of acid is sour in taste, it turns blue litmus red and neutralizes bases. Whereas aqueous solution of base is bitter in taste. It turns red litmus blue or neutralizes acids. salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. In this section of Acids, Bases and Salts Beet root Solution, Indicator prepared from Red Cabbage Leaves, Chemical Properties of Acids and Bases, Common Acids and Bases used in Laboratory, Concentrated and Dilute acids, Definition of Acids and Bases, Indicators, Llitmus and Dry Turmeric Indicator, Methyl Orange and Phenolphthalein Indicators, Olfactory Indicators, Organic and Inorganic Acids, Oxo acids and Hydrated Acids, Reaction of Acids and Bases, Reaction of Metals with Acids and Bases, Strength of Acids and Bases, etc. have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
- Sample Test(s)Test NameSubject(s)Topics / ChaptersQuestions / MarksActionTutorial - 10th - Chemistry [Acids Bases and Salts I]ChemistryAcids Bases and Salts I10 / 10View All FREE Test(s)
An acid and a base are substances in chemistry. The aqueous solution of acid is sour in taste, it turns blue litmus red and neutralizes bases. Whereas aqueous solution of base is bitter in taste. It turns red litmus blue or neutralizes acids. salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. In this section of Acids, Bases and Salts Acids and Physical Properties of Acids, Bases and Physical Properties of Bases, Chlor Alkali Process, Classification of Salts, Common Salts in Daily Life, General Properties of Salts, Importance of pH in Daily Life, Important Chemical Compounds, pH of Salts, Preparation of Salts, Salts, etc. have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
- Sample Test(s)Test NameSubject(s)Topics / ChaptersQuestions / MarksActionTutorial - 10th - Chemistry [Acids Bases and Salts II]ChemistryAcids Bases and Salts II10 / 10View All FREE Test(s)
Materials can be divided into metals and nonmetals. In this section of Metals and Non Metals Metal React With Water, Metals and Non-Metals, Metals Burnt in Air, Metals React With Acids, Metals React With Other Metal Salts, Physical Property of Metal - Conductivity, Density, Ductility, Hardness, Physical Property of Metal - Melting Point and Boiling Point, Physical Property of Metal - Physical State, Physical Property of Metal - Sonority, Physical Property of Metal Appearance, Physical Property of Non Metal, , etc. have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
- Sample Test(s)Test NameSubject(s)Topics / ChaptersQuestions / MarksActionTutorial - 10th - Chemistry [Metals and Non Metals I]ChemistryMetals and Non Metals I10 / 10View All FREE Test(s)
Materials can be divided into metals and nonmetals. In this section of Metals and Non Metals Alloys and its Importance, Conductivity of Ionic Compounds, Corrosion and its Prevention, Different types of ores, Enrichment or Dressing of an Ore, Extraction of metals at the bottom of the Activity Series of High Activity, Extraction of metals at the bottom of the Activity Series of Low Activity, Extraction of Metals at the middle of the activity Series of Medium Reactivity, Melting and Boiling Point of Ionic Compounds, Metallurgical Operations, Metallurgy and its Principles, Mineral and Ores, etc. have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
- Sample Test(s)Test NameSubject(s)Topics / ChaptersQuestions / MarksActionTutorial - 10th - Chemistry [Metals and Non Metals II]ChemistryMetals and Non Metals II10 / 10View All FREE Test(s)
The element Carbon is a nonmetal, its symbol is C. The atomic number of carbon is 6 mass number is 12. In this section of Carbon and Its Compounds Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes, Allotropes of Carbon, Carbon - As an Element, Covalent and Ionic Bonds, Diamonds, Differences between Organic and Inorganic Compounds, Fullerene, Graphite, Hydro-Carbons, Organic Chemistry, Property of Carbon Compounds- Bond Strength, Property of Carbon Compounds- Catenation, Property of Carbon Compounds- Isomerism, Property of Carbon Compounds- Multiple Bond Formation, Property of Carbon Compounds- Tetravalency, Saturated and Unsaturated Hydro Carbons, etc. have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
- Sample Test(s)Test NameSubject(s)Topics / ChaptersQuestions / MarksActionTutorial - 10th - Chemistry [Carbon and Its Compounds I]ChemistryCarbon and Its Compounds I10 / 10View All FREE Test(s)
The Chemistry of Carbon Compound is called Organic Chemistry. Carbon forms a large number of compounds. In this section of Carbon and Its Compounds Addition Reaction, Alcohol Functional Group, Aldehyde Functional Group, Carboxylic Acid Functional Group, Effect of Ethanol on Human Beings, Esterification and Saponification, Ethanol, Ethnoic Acid, Flames, Fossil Fuels, Functional Groups, Halogens Functional Group, Homologous Series, Ketone Functional Group, Nomenclature of Carbon Compounds, Oxidation of Carbon Compounds, Soaps and Detergents, Sources of Organic Compounds, Subsitution Reaction of Carbon Compounds, etc. have been explained. Watch the videos and master the concepts
Explore Concepts (Click & View)
- Types of changes
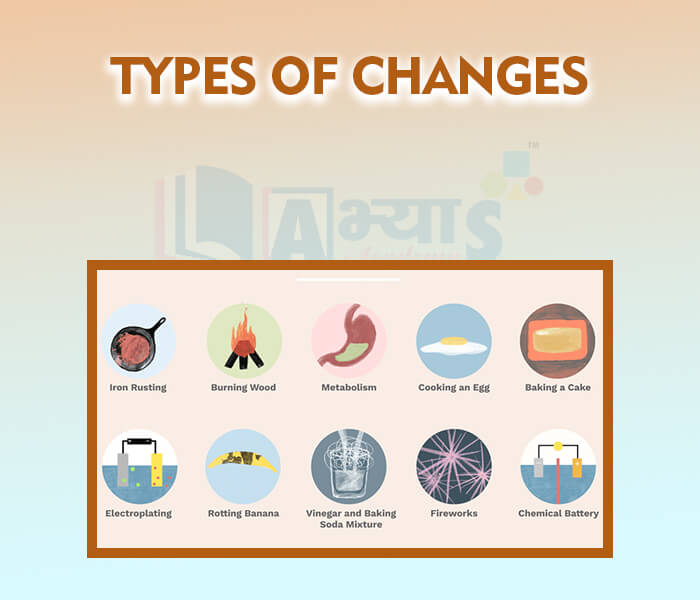
- Physical Change

- Chemical changes

- Chemical Reaction

- Reactant
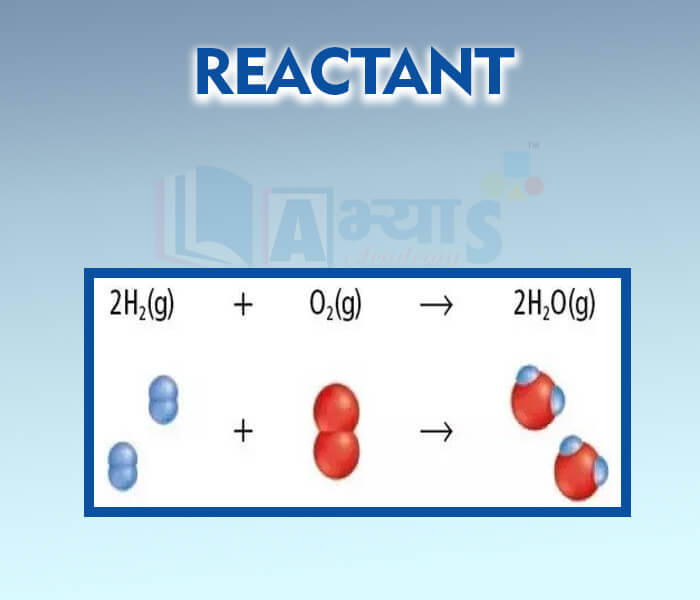
- Product

- Characteristics of chemical Reactions
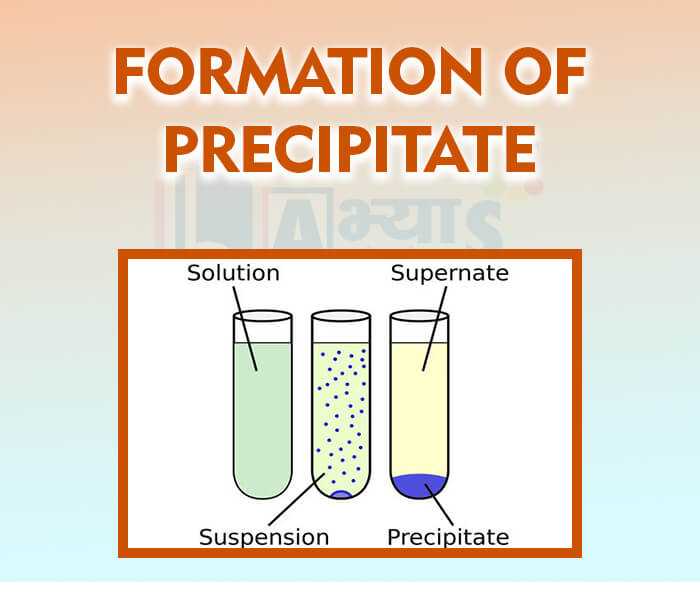
- Evolution of gas

- Formation of precipitate
- Change in Temperature

- Endothermic and Exothermic Reaction
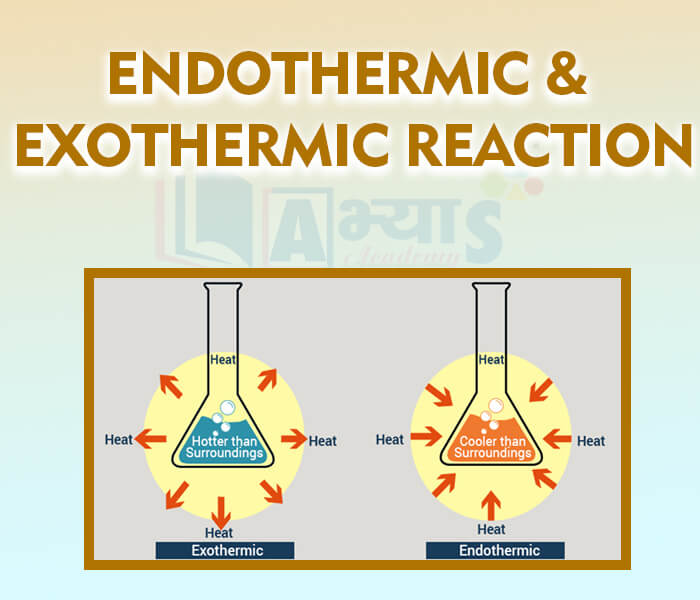
- Change in Colour

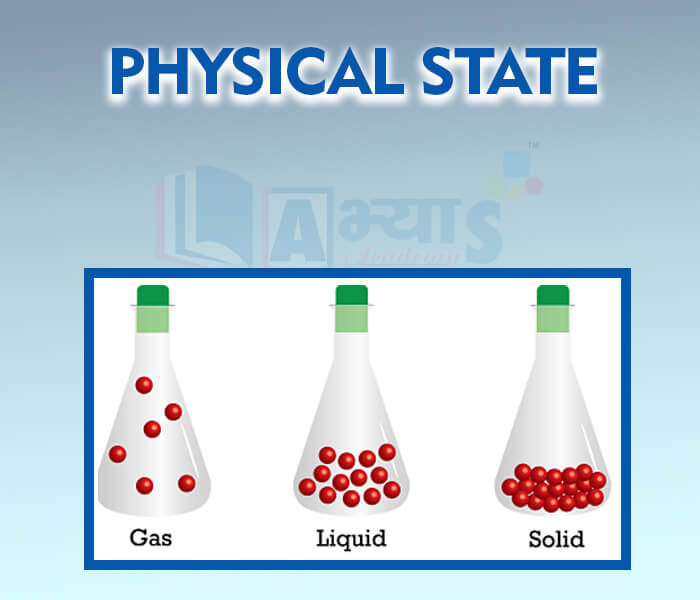
- Physical State
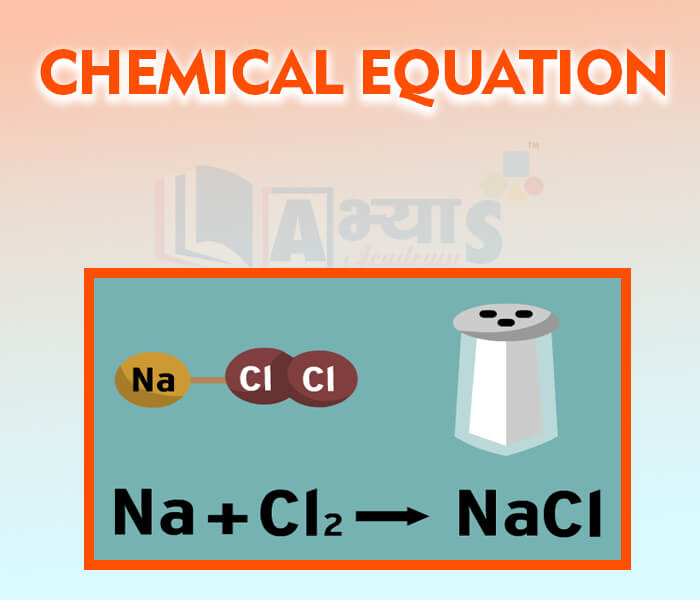
- Chemical Equation
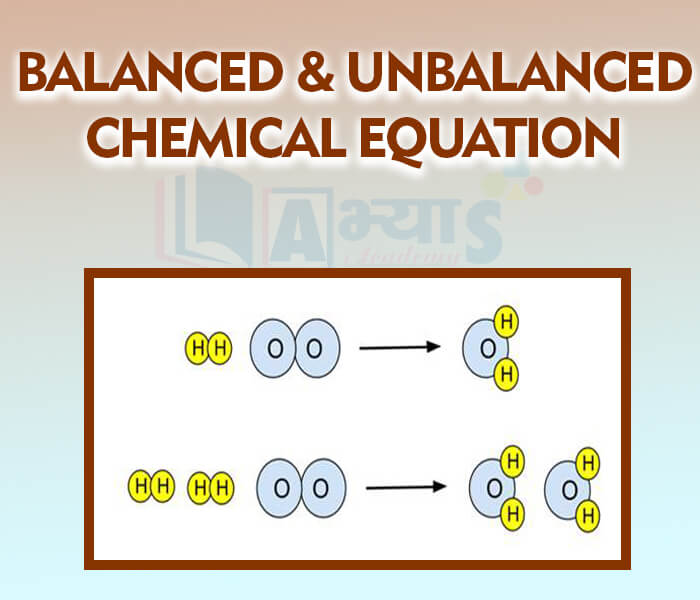
- Balanced and Unbalanced Chemical Equation
- Information conveyed by a chemical equation
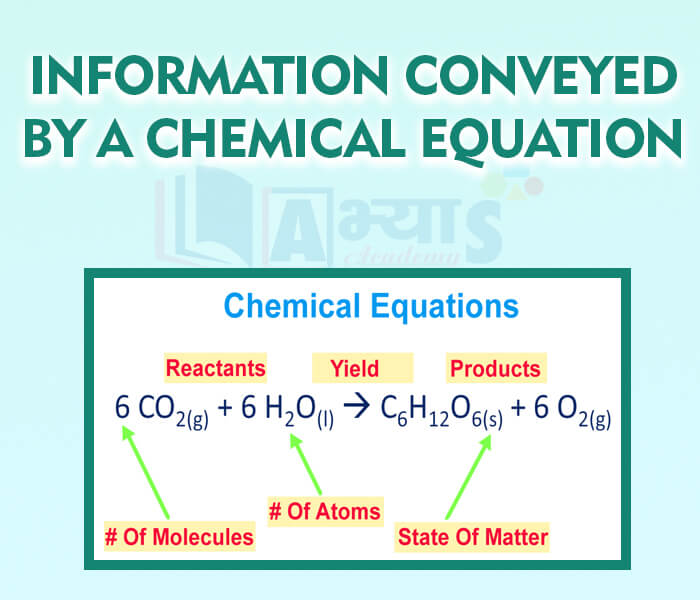
- Advantages of using a chemical reaction

- Limitations of chemical Reaction

- How to make equations more informative

- Corrosion

Explore Concepts (Click & View)
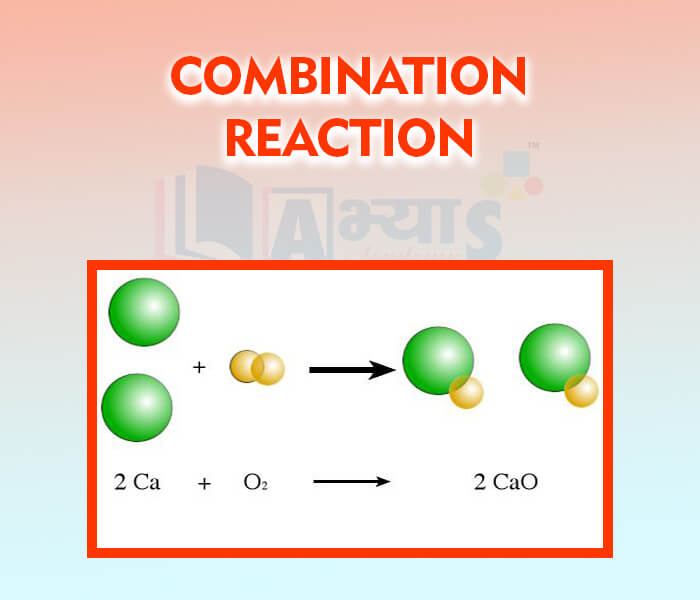
- Combination Reaction
- Representation of Chemical Reaction
- Decomposition Reaction

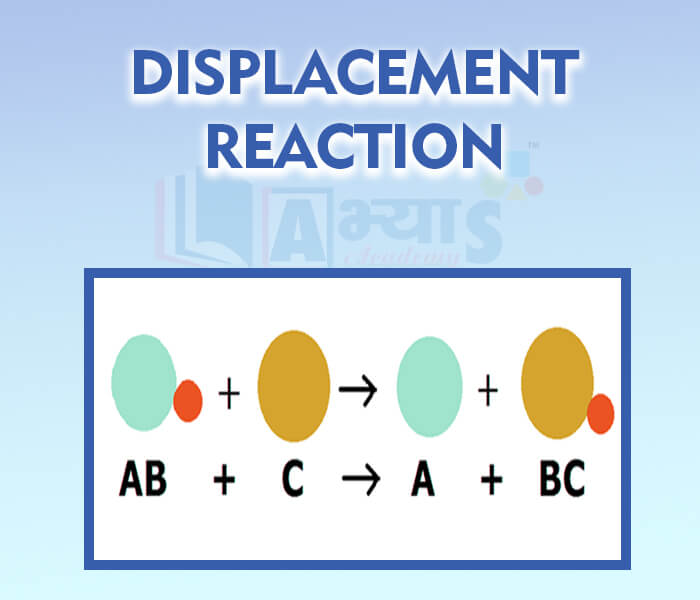
- Displacement Reaction
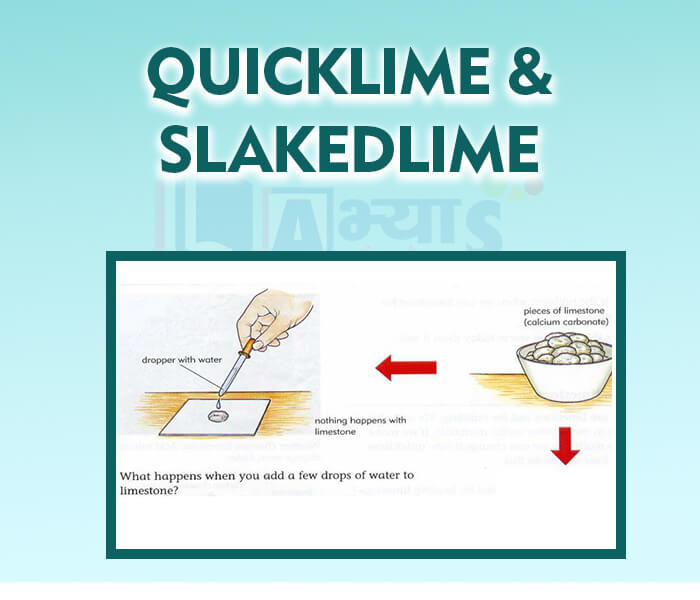
- Quicklime and Slaked Lime
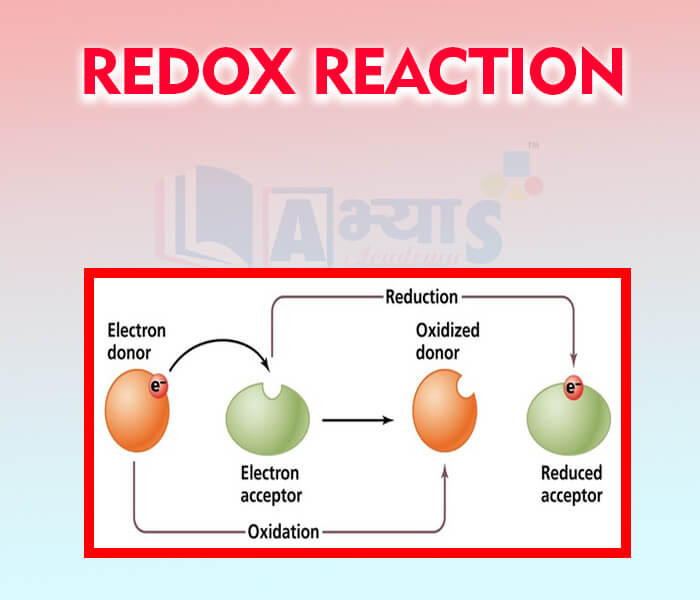
- Redox Reaction
- Rancidity

Explore Concepts (Click & View)
- Definition of Acids and Bases

- Acids and Physical Properties of Acids

- Oxo acids and Hydrated Acids

- Organic and Inorganic Acids

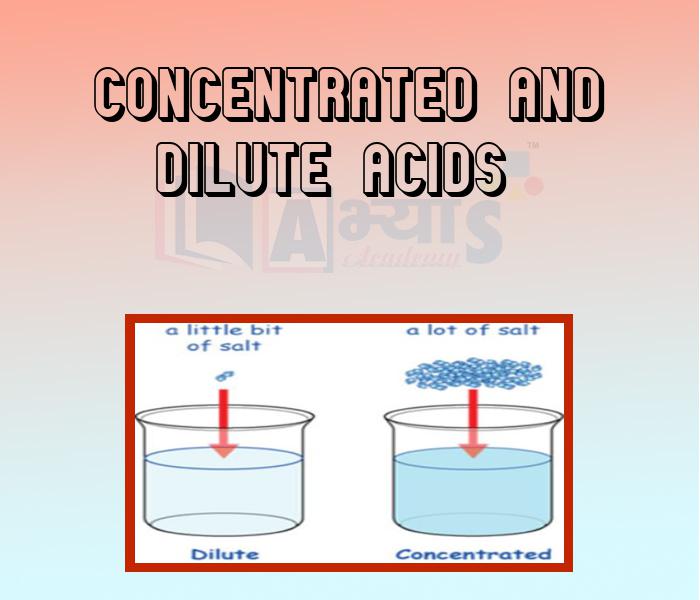
- Concentrated and Dilute acids
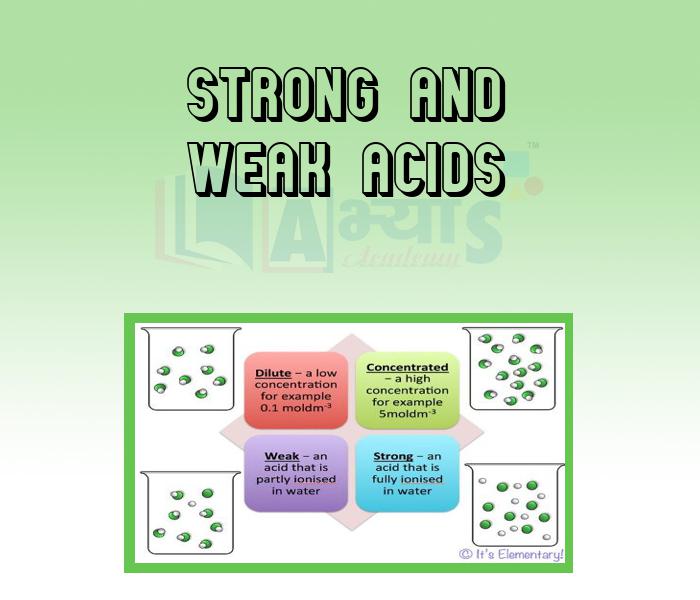
- Strong and Weak Acids
- Uses of Acids

- Uses of Bases

- Bases and Physical Properties of Bases
- Chemical Properties of Acids and Bases

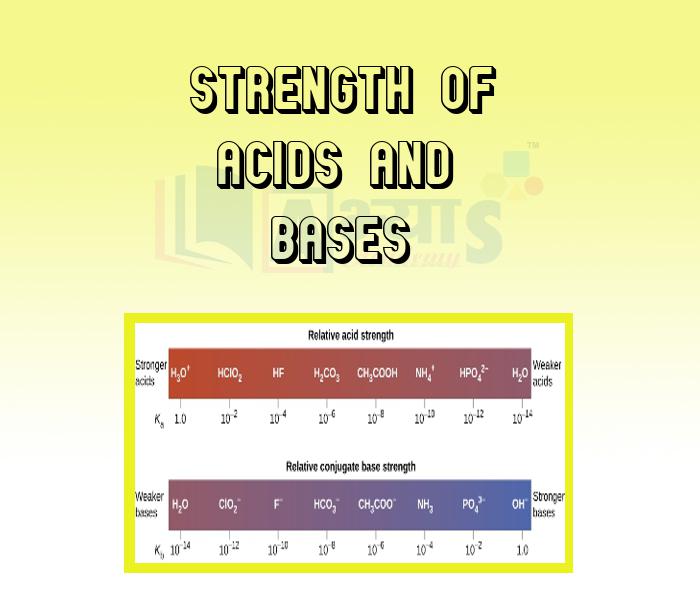
- Strength of Acids and Bases
- Indicators
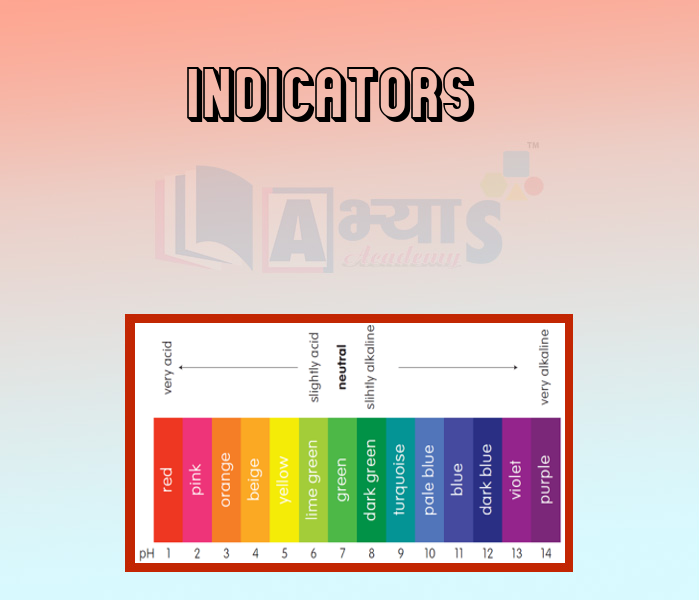
- Universal Indicators

- Reaction of Metals with Acids and Bases

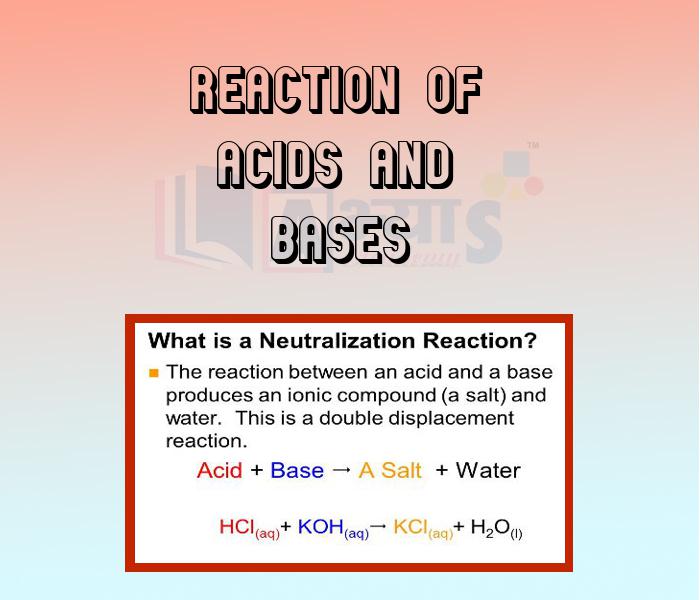
- Reaction of Acids and Bases
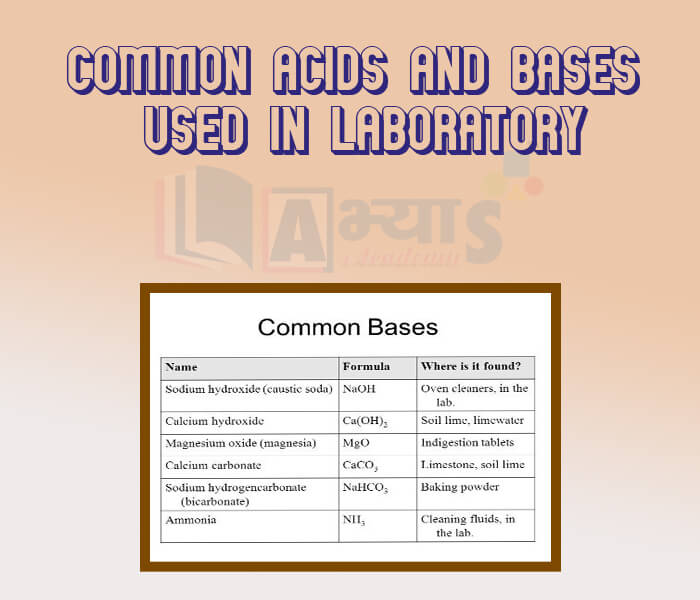
- Common Acids and Bases used in Laboratory
- Litmus and Dry Turmeric Indicator

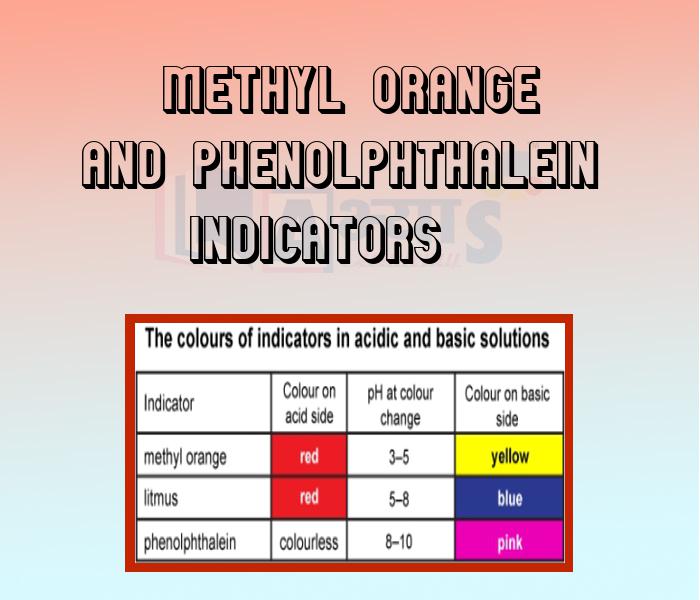
- Methyl Orange and Phenolphthalein Indicators
- Olfactory Indicators

- Beet root Solution, Indicator prepared from Red Cabbage Leaves

Explore Concepts (Click & View)
- Salts

- Classification of Salts

- Preparation of Salts

- General Properties of Salts

- pH of Salts

- Importance of pH in Daily Life

- Common Salts in Daily Life

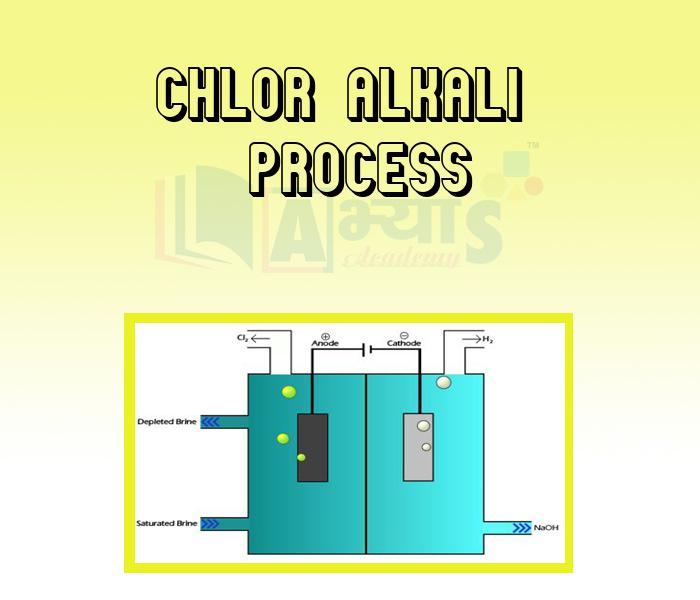
- Chlor Alkali Process
- Important Chemical Compounds

Explore Concepts (Click & View)
- Metals and Non-Metals

- Physical Property of Metal - Physical State

- Physical Property of Metal - Ductility

- Physical Property of Metal - Conductivity

- Physical Property of Metal Appearance

- Physical Property of Metal - Hardness

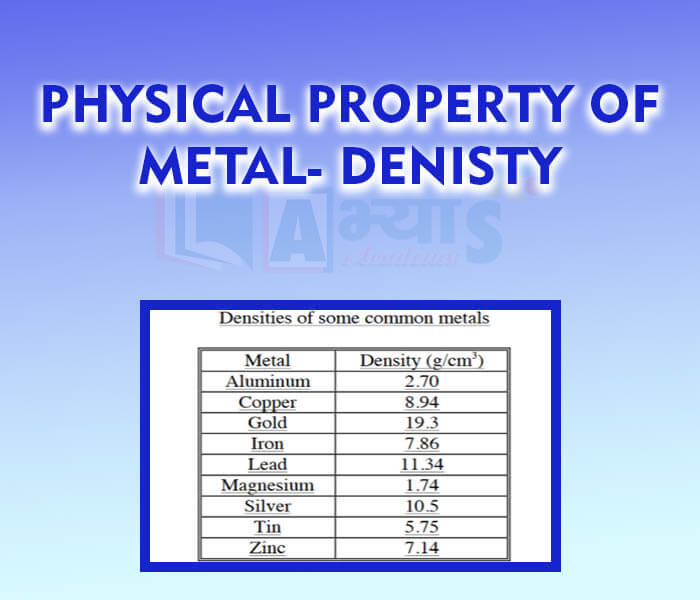
- Physical Property of Metal - Denisty
- Physical Property of Metal - Melting Point and Boiling Point

- Physical Property of Metal - Sonority

- Reactivity Series

- Physical Property of Non-Metal - Physical State

- Physical Property of Non-Metal - Conductivity

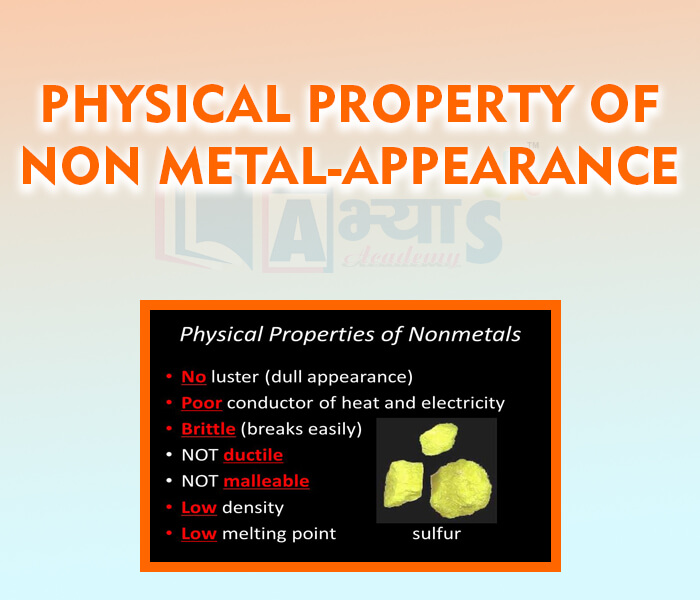
- Physical Property of Non-Metal - Appearance
- Physical Property of Non-Metal - Hardness

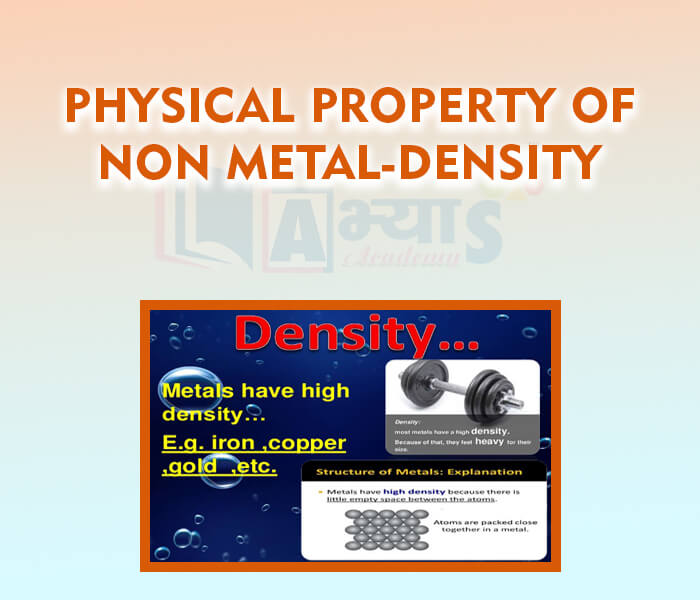
- Physical Property of Non-Metal - Density
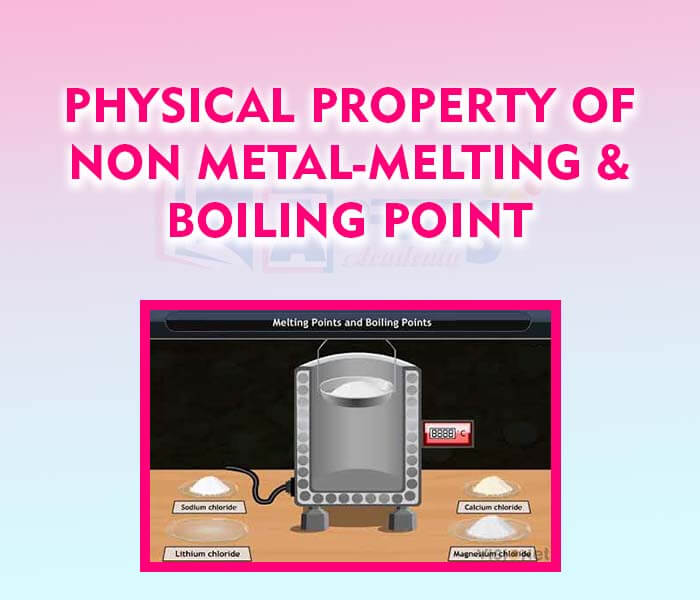
- Physical Property of Non-Metal - Melting and Boiling Point
- Physical Property of Non-Metal - Sonority

- Reaction with Oxygen

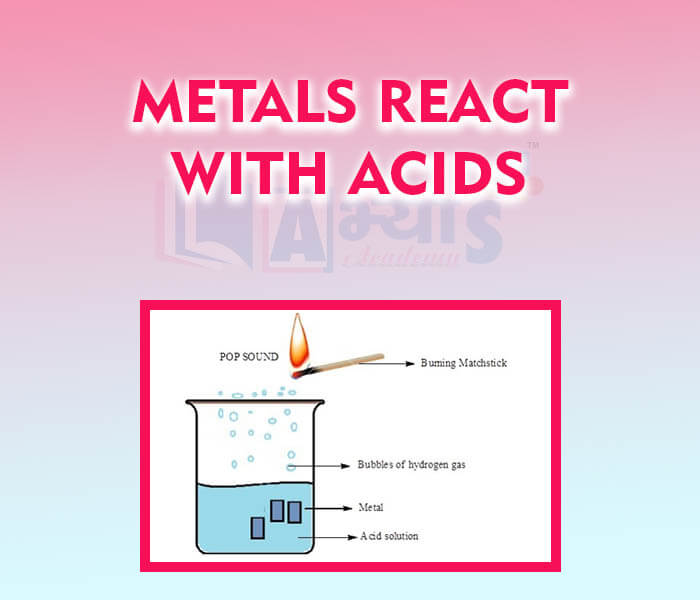
- Metals React With Acids
- Reaction With Water

- Uses of Metals

- Metals React With Other Metal Salts

- Uses of Non Metals

Explore Concepts (Click & View)
- Mineral and Ores

- Different types of ores

- Metallurgy and its Principles

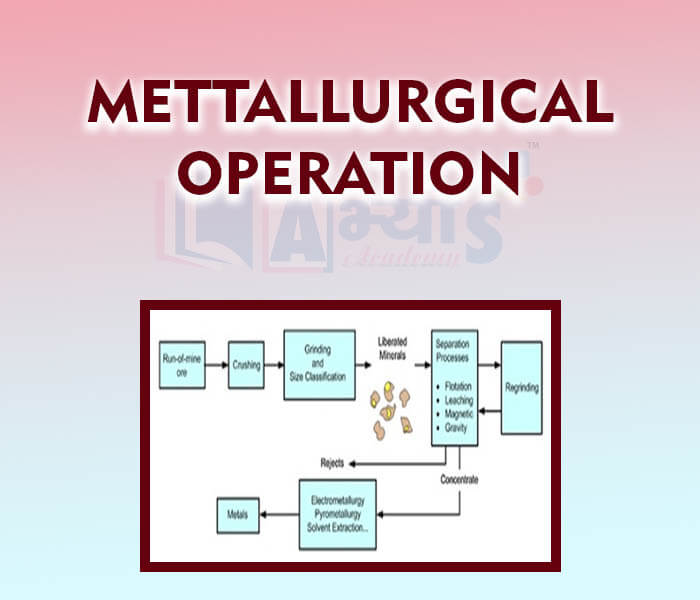
- Metallurgical Operations
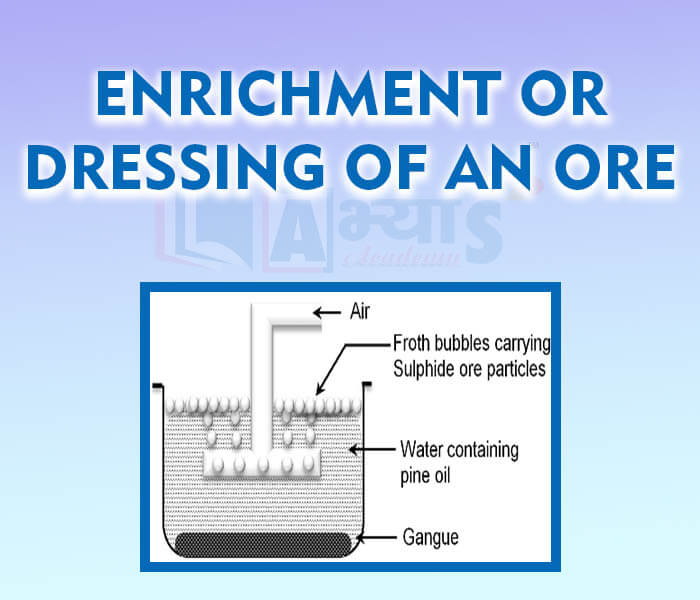
- Enrichment or Dressing of an Ore
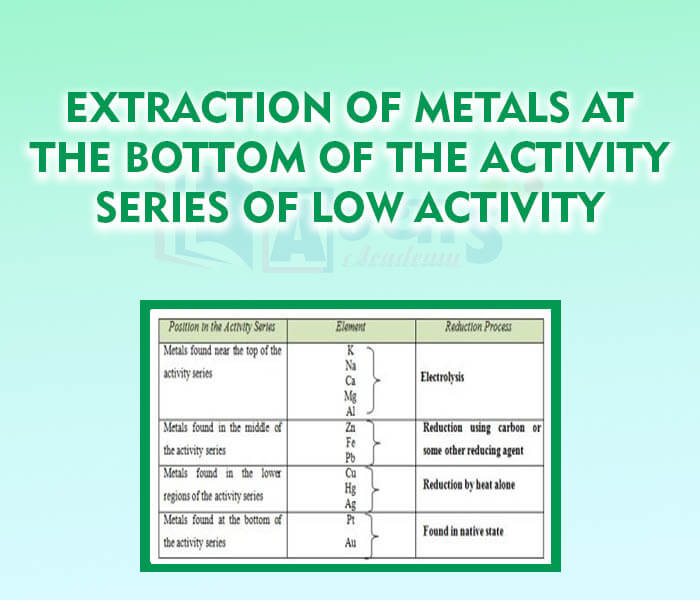
- Extraction of metals at the bottom of the Activity Series of Low Activity
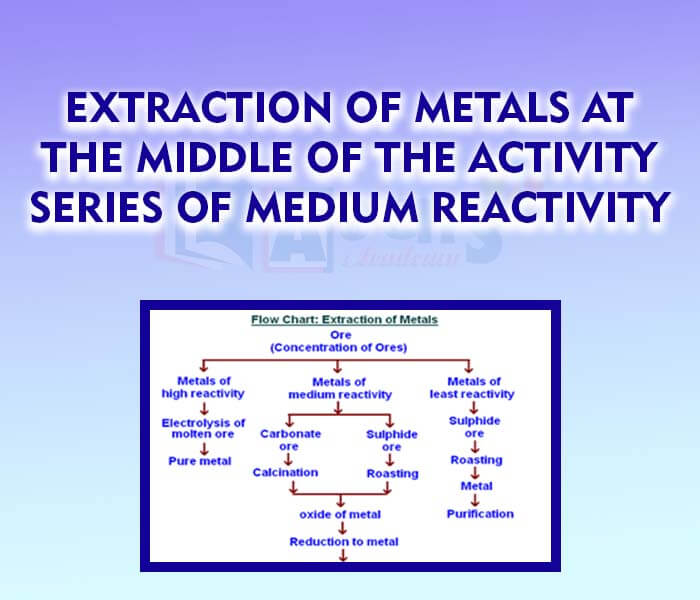
- Extraction of Metals at the middle of the activity Series of Medium Reactivity
- Extraction of metals at the top of the Activity Series of High Activity

- Refining of Metals
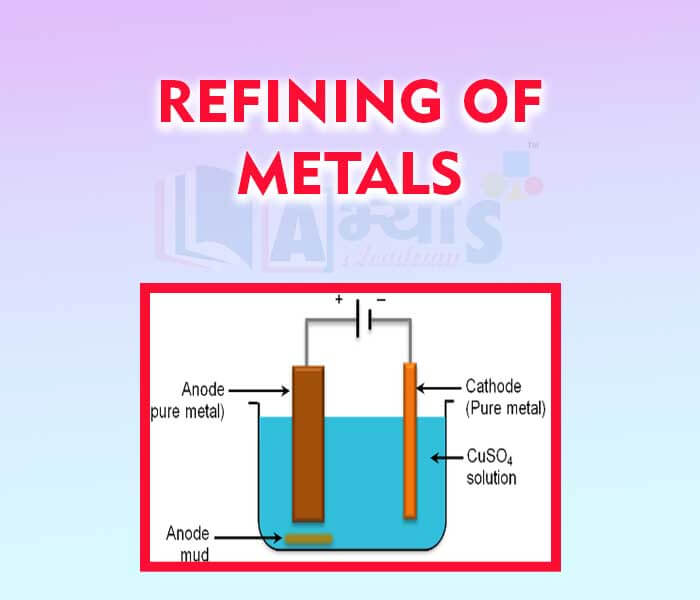
- Corrosion and its Prevention

- Alloys and its Importance

- Physical Nature of Ionic Compounds

- Solubility of Ionic Compounds

- Melting and Boiling Point of Ionic Compounds

- Conductivity of Ionic Compounds
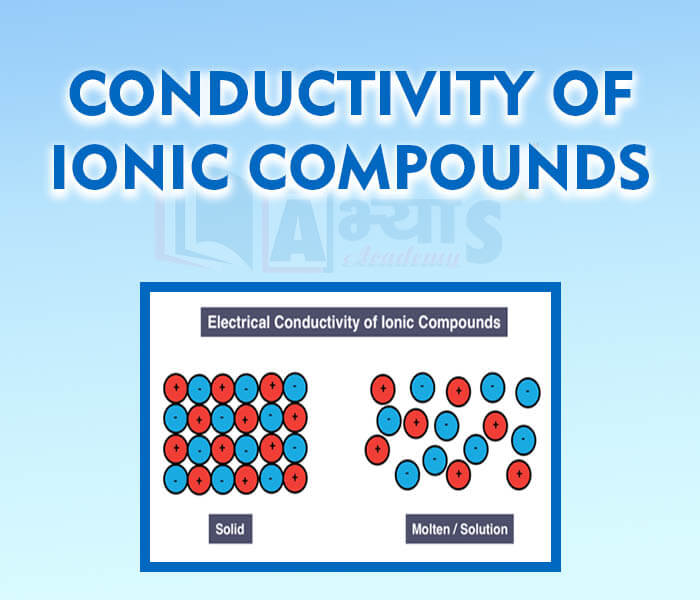
Explore Concepts (Click & View)
- Carbon - As an Element

- Covalent and Ionic Bonds

- Allotropes of Carbon
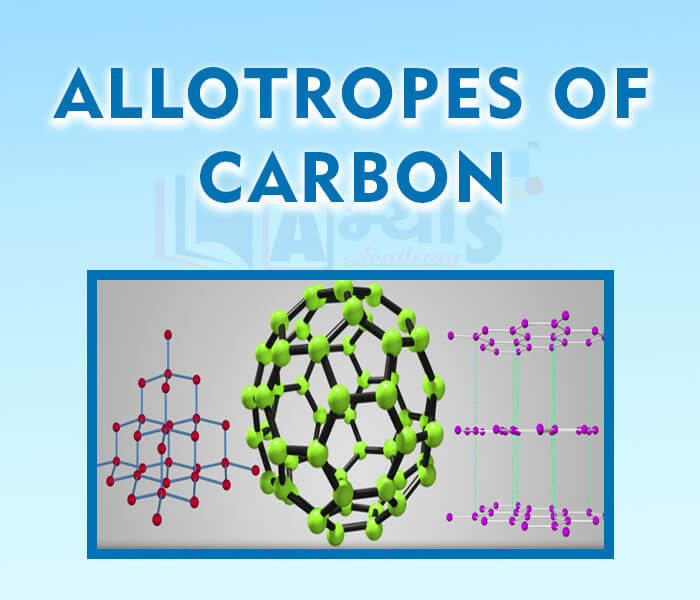
- Diamonds

- Graphite

- Fullerene
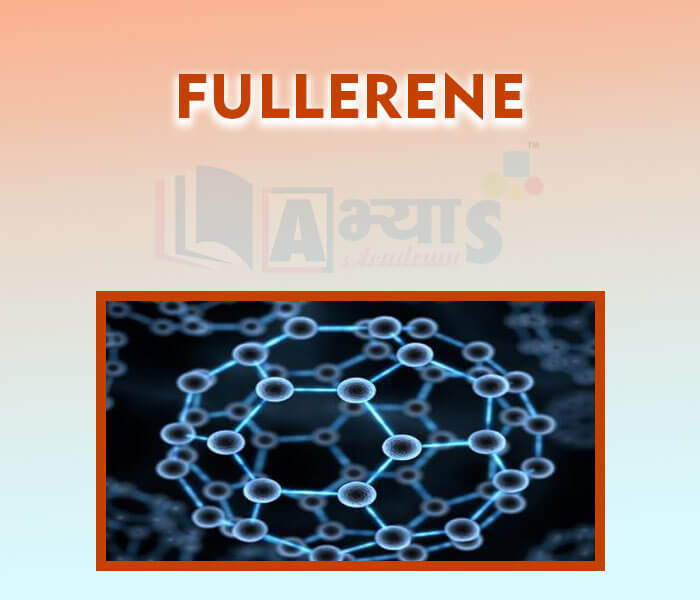
- Differences between Organic and Inorganic Compounds

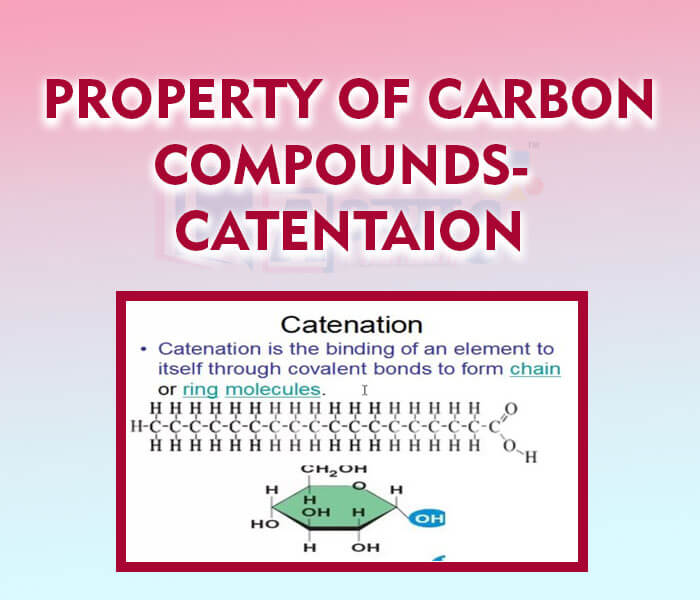
- Property of Carbon Compounds- Catenation
- Property of Carbon Compounds- Tetravalency

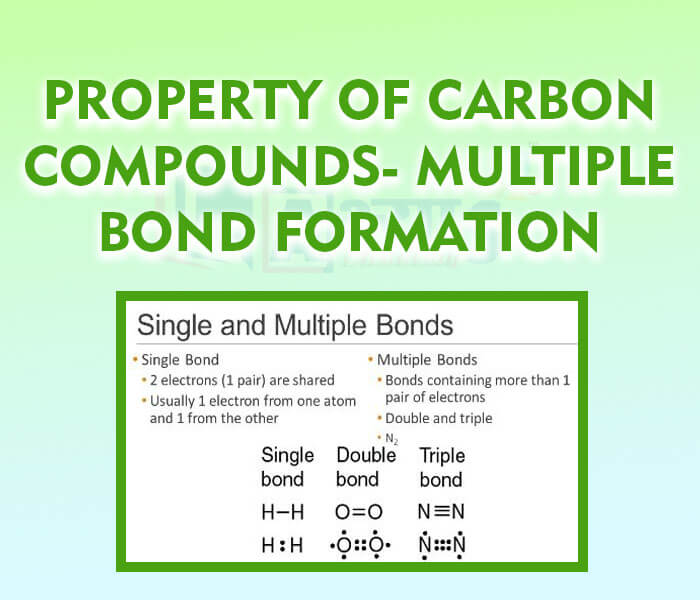
- Property of Carbon Compounds- Multiple Bond Formation
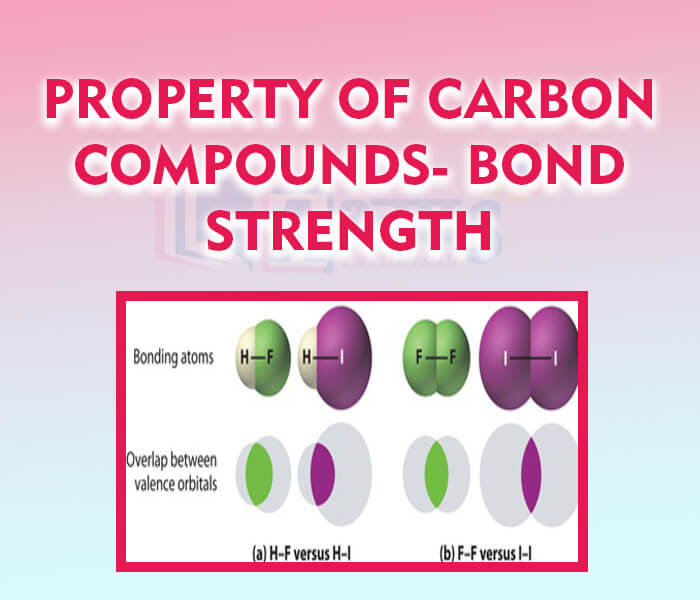
- Property of Carbon Compounds- Bond Strength
- Organic Chemistry
- Hydro-Carbons

- Saturated and Unsaturated Hydro Carbons
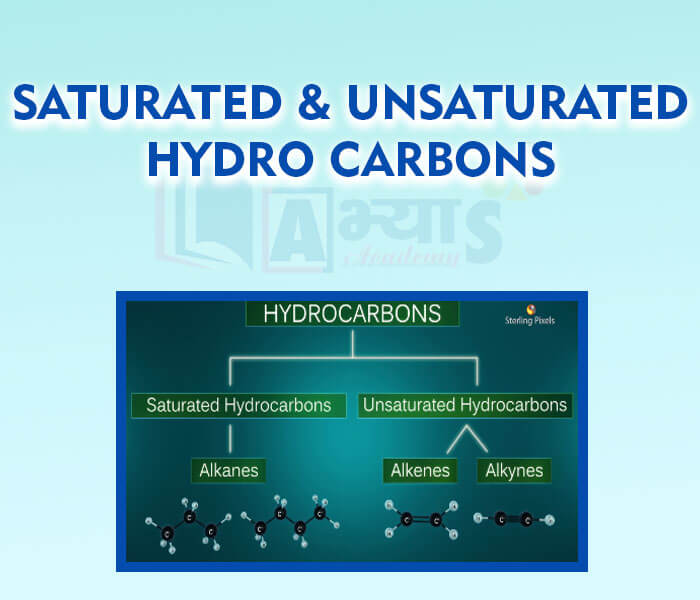
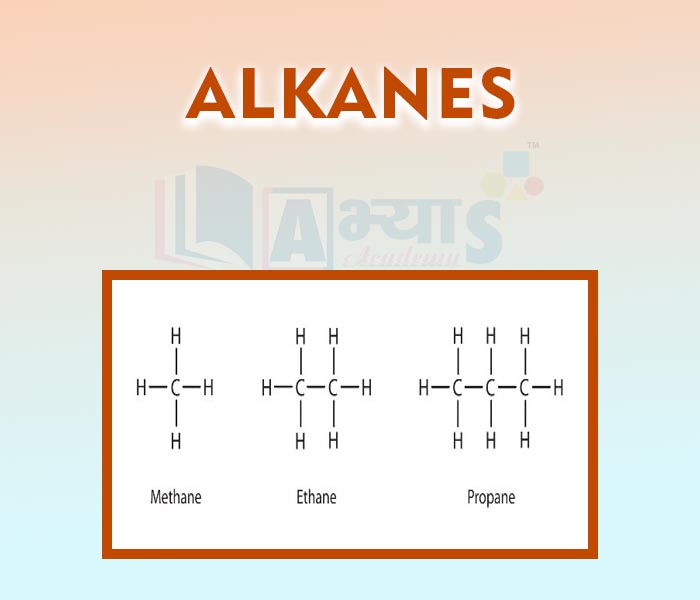
- Alkanes
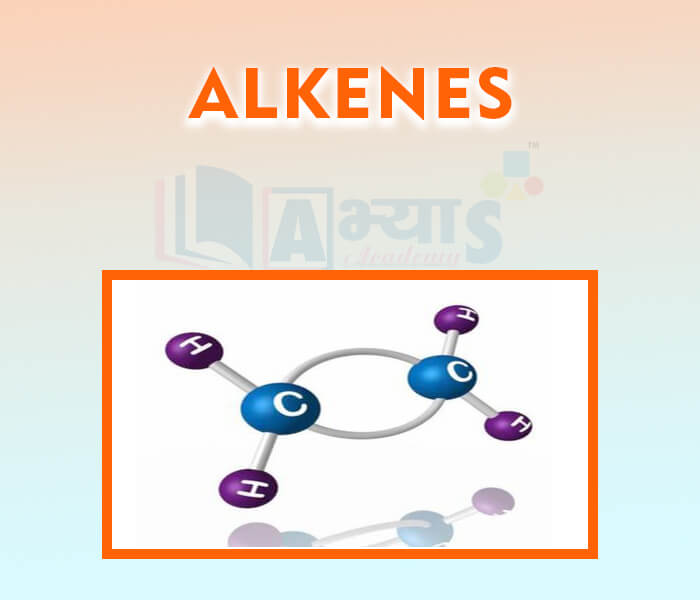
- Alkenes
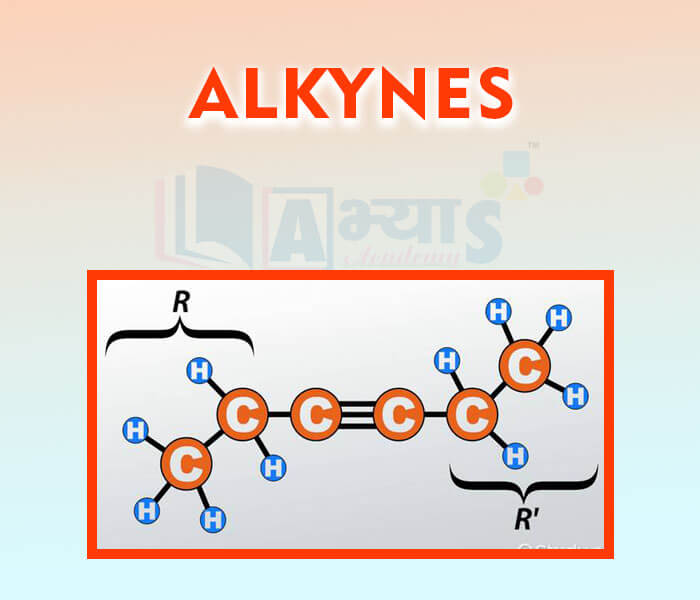
- Alkynes
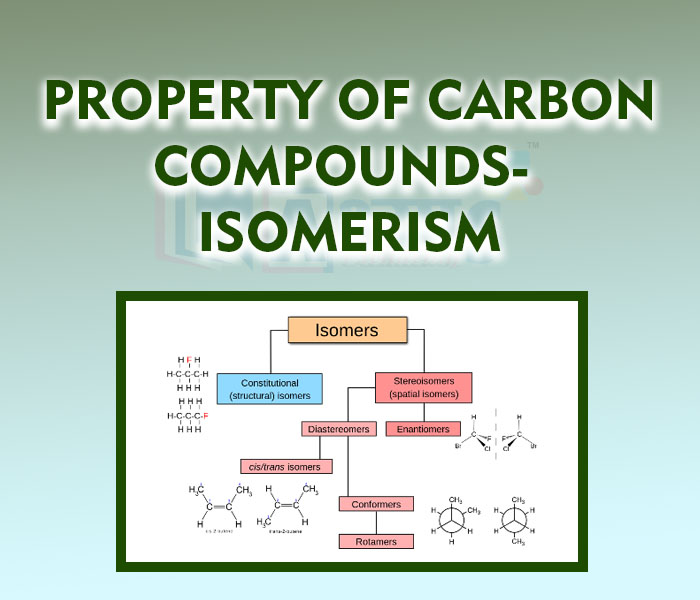
- Property of Carbon Compounds- Isomerism
Explore Concepts (Click & View)
- Functional Groups

- Homologous Series

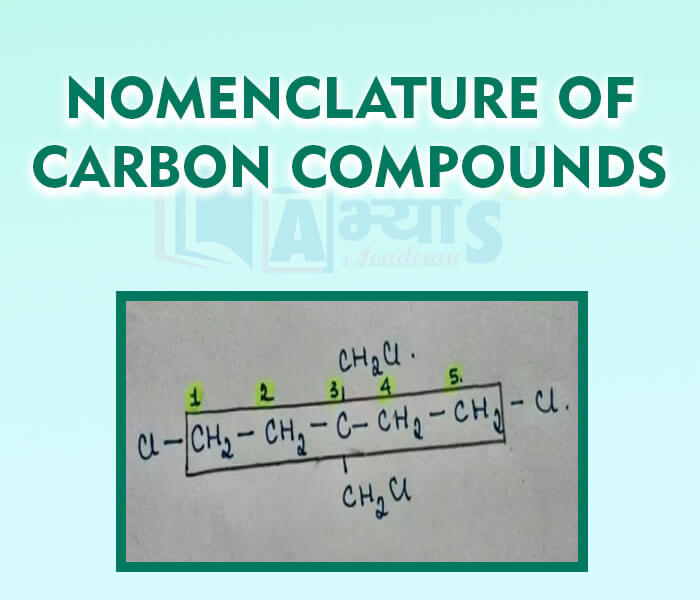
- Nomenclature of Carbon Compounds
- Combustion of Carbon Compounds

- Oxidation of Carbon Compounds

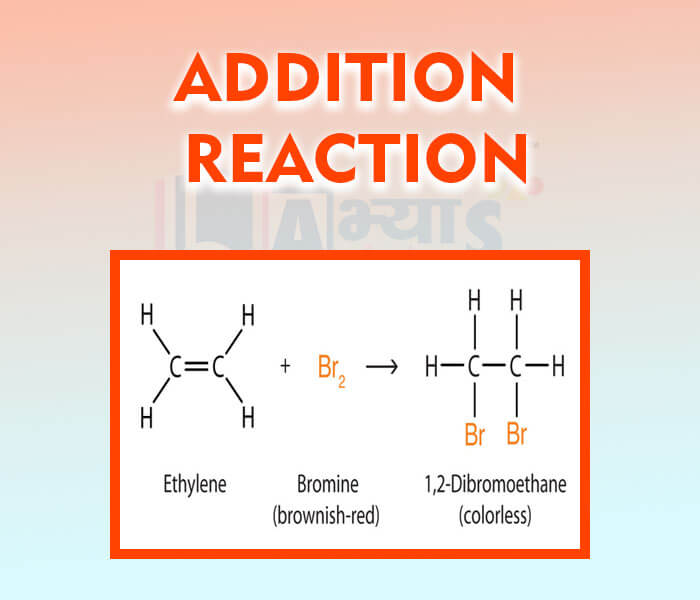
- Addition Reaction
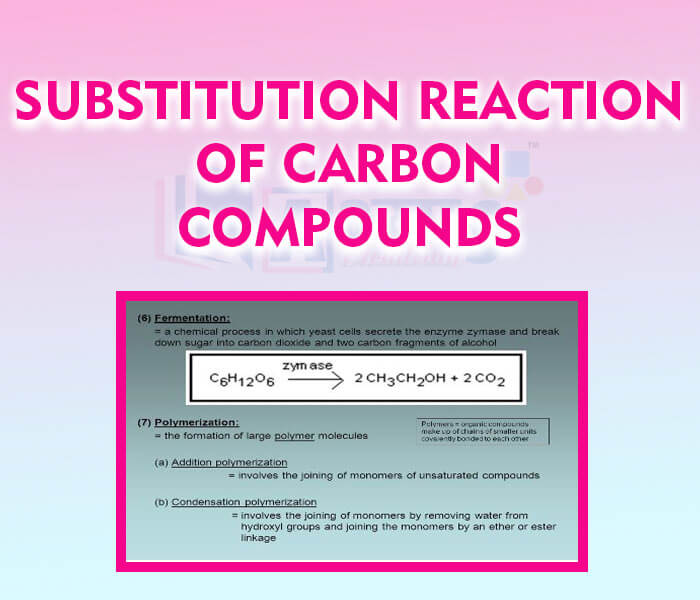
- Subsitution Reaction of Carbon Compounds
- Fossil Fuels

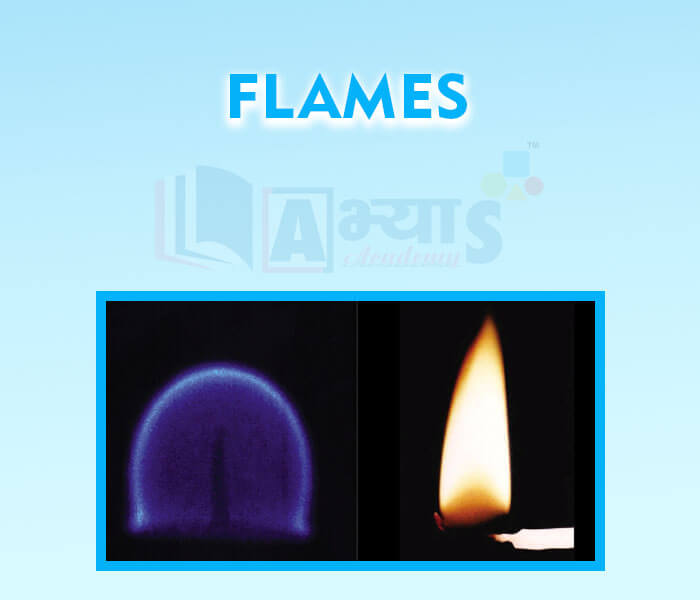
- Flames

- Ethanol

- Effect of Ethanol on Human Beings

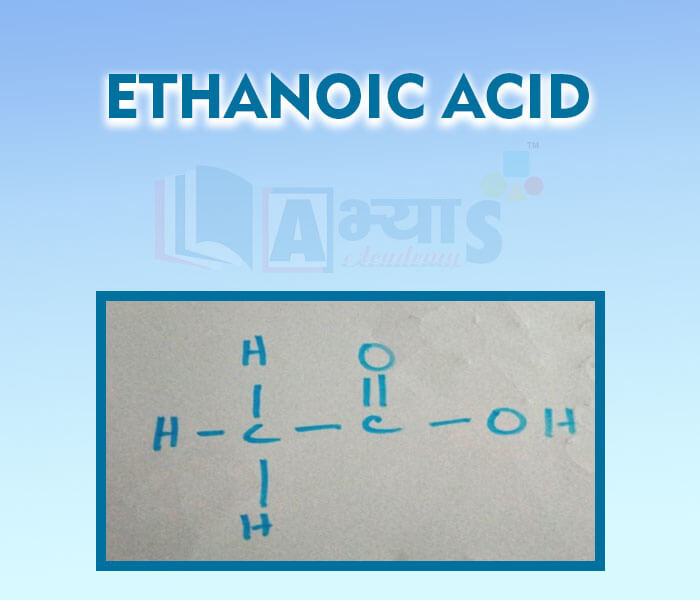
- Ethnoic Acid
- Esterification and Saponification

- Soaps and Detergents

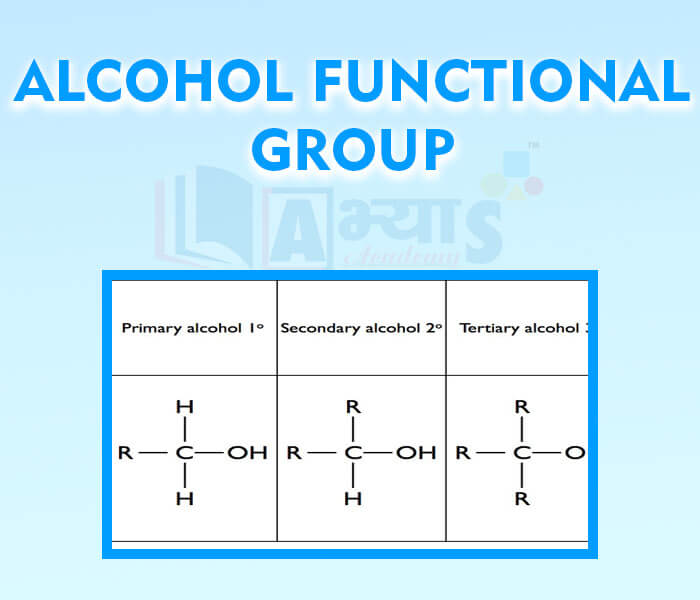
- Alcohol Functional Group
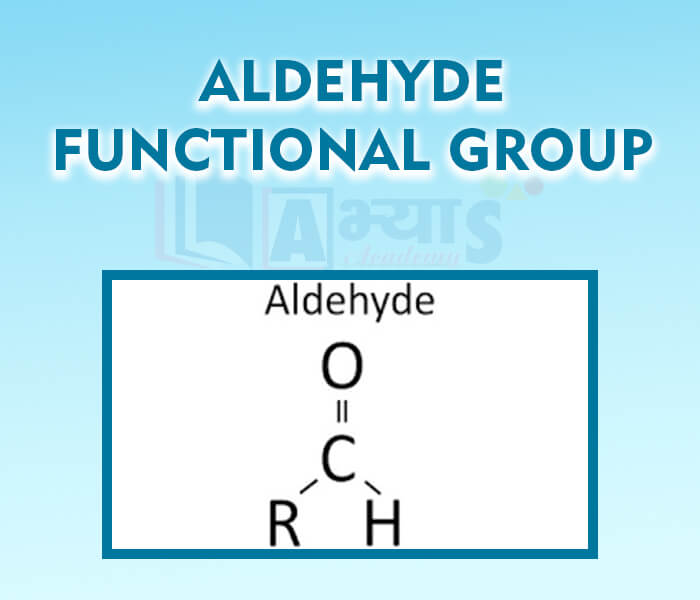
- Aldehyde Functional Group
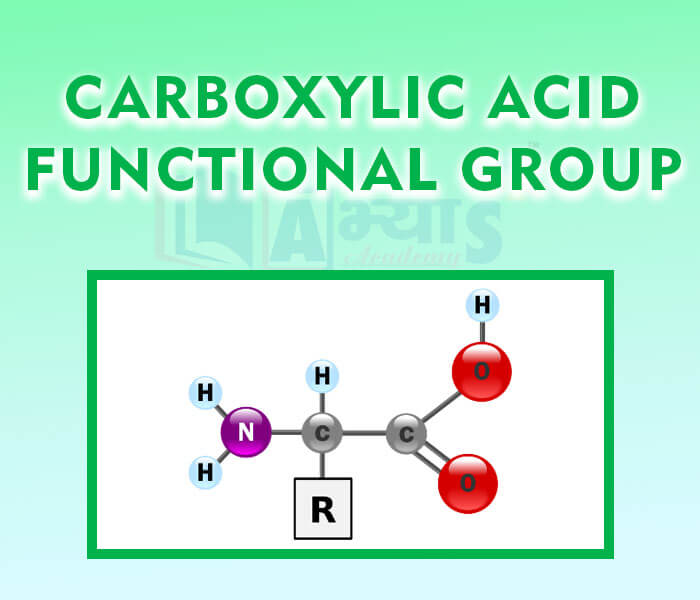
- Carboxylic Acid Functional Group
- Halogens Funcational Group
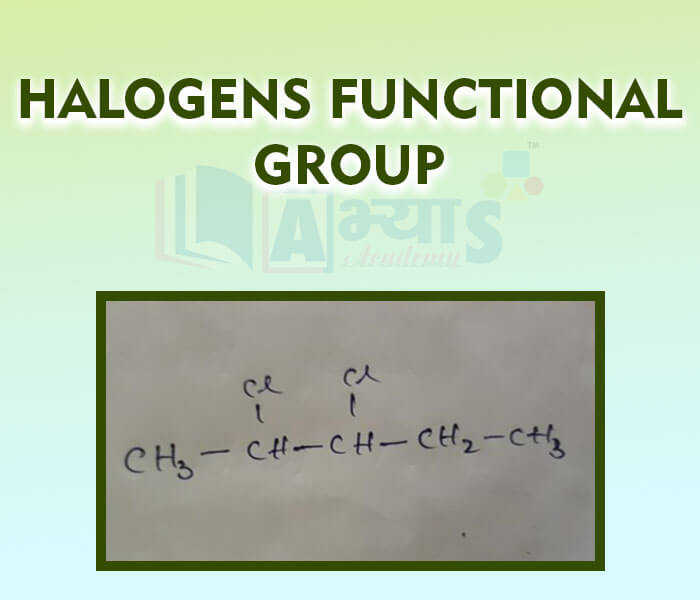
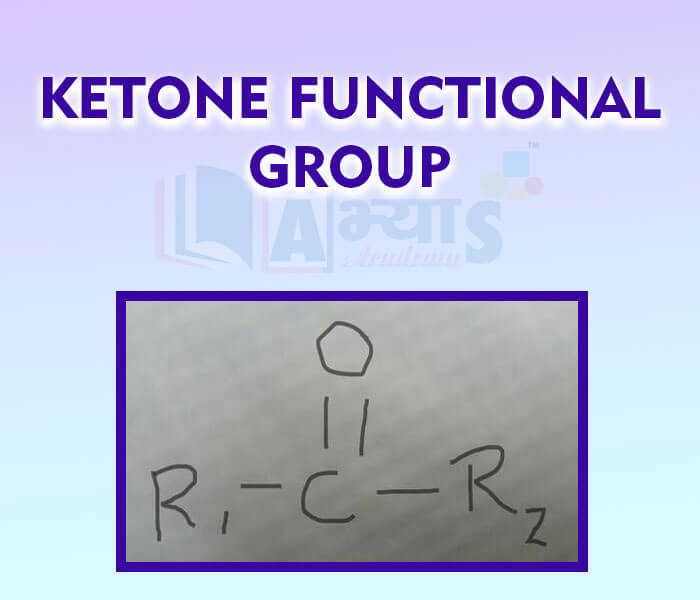
- Ketone Functional Group
- Sources of Organic Compounds
Students / Parents Reviews [20]
Third consective year,my ward is in Abhyas with nice experience of admin and transport support.Educational standard of the institute recumbent at satisfactory level. One thing would live to bring in notice that last year study books was distributed after half of the session was over,though study ...

Ayan Ghosh
8thThe experience was nice. I studied here for three years and saw a tremendous change in myself. I started liking subjects like English and SST which earlier I ran from. Extra knowledge gave me confidence to overcome competitive exams. One of the best institutes for secondary education.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.

Shreya Shrivastava
8thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thUsually we see institutes offering objective based learning which usually causes a lag behind in subjective examinations which is the pattern followed by schools. I think it is really a work of planning to make us students grab the advantages of modes of examination, Objective Subjective and Onli...

Anika Saxena
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thMy experience with Abhyas Academy has been very good. When I was not in Abhyas whenever teacher ask questions I could not speak it confidently but when I came in Abhyas, my speaking skills developed and now I am the first one to give the answer of teachers question.

Upmanyu Sharma
7thAbhyas institute is one of the best coaching institute in the vicinity of Ambala cantt.The institute provides good and quality education to the students.The teachers are well experienced and are very helpful in solving the problems. The major advantages of the institute is extra classes for weak...

Shreya Shrivastava
8thAbhyas is an institute of high repute. Yogansh has taken admission last year. It creates abilities in child to prepare for competitive exams. Students are motivated by living prizes on basis of performance in Abhyas exams. He is satisfied with institute.

Yogansh Nyasi
7thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thAbhyas institute is one of the best coaching institute in the vicinity of Ambala Cantt area. The teachers of the institute are well experienced and very helpful in solving the problems of the students.The good thing of the institute is that it is providing extra classes for the students who are w...

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very nice or it can be said wonderful. I have been studying here from seven class. I have been completing my journey of three years. I am tinking that I should join Abhyas Academy in tenth class as I am seeing much improvement in Maths and English

Hridey Preet
9thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thWhen I have not joined Abhyas Academy, my skills of solving maths problems were not clear. But, after joining it, my skills have been developed and my concepts of science and SST are very well. I also came to know about other subjects such as vedic maths and reasoning.

Sharandeep Singh
7thWe started with lot of hope that Abhyas will help in better understnding of complex topics of highers classes. we are not disappointed with the progress our child has made after attending Abhyas. Though need to mention that we expected a lot more. On a scale of 1-10, we would give may be 7.

Manya
8thAbhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.









